
Playing It Safe On Line
Secretary Tim gave a talk on Cyber Security or in others words protecting yourself, your family and your business when working on line and accessing or sending emails.
Fraud and malevolent software are costing Australians and businesses approximately $17 billion dollars a year and rising rapidly.
There is much that we can do as individuals to protect ourselves, The Australian Signals Directorate provides a plethora of information on what individuals, businesses and organisations can do to avoid, fraud, theft, or malware. Below are what they call their essential 8 strategies and you can access more information at

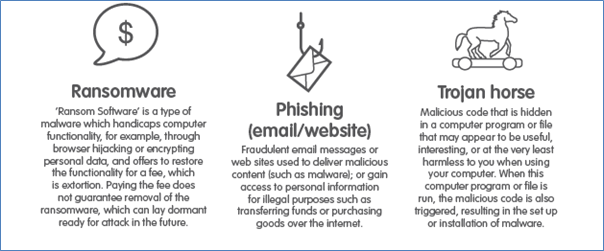

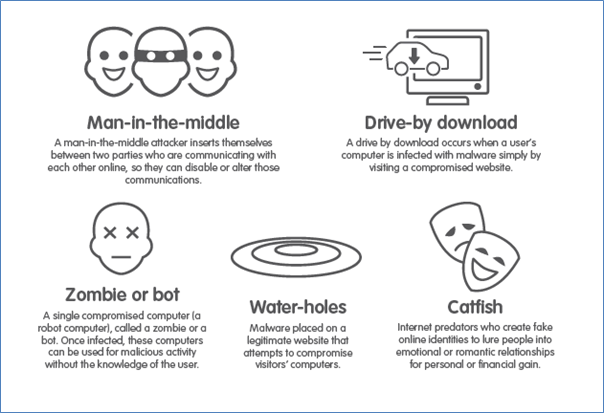

The Essential Eight
To prevent malware running:
Application Whitelisting TOP 4 A whitelist only allows selected software applications to run on computers. Why? All other software applications | Application Patching TOP 4 A patch fixes security vulnerabilities in software applications. Why? Adversaries will use known security vulnerabilities to target computers. |
Disable untrusted Microsoft Office macros Microsoft Office applications can use software known as “macros” to automate routine tasks. Why? Macros are increasingly being used to enable the download of malware. Adversaries can then access sensitive information, so macros should be secured or disabled. | User application hardening Block web browser access to Adobe Flash player (uninstall if possible), web advertisements and untrusted Java code on the internet. Why? Flash, Java and web ads have long been popular ways to deliver malware to infect computers. |
To limit the extent of incidents and recover data:
Restrict administrative privileges TOP 4 Only use administrator privileges for managing systems, installing legitimate software and applying software patches. These should be restricted to only those that need them. Why? Admin accounts are the ‘keys to the kingdom’, adversaries use these accounts for full access to information and systems. | Patching operating systems TOP 4 A patch fixes security vulnerabilities in operating systems. Why? Adversaries will use known security vulnerabilities to target computers. |
Multi-factor authentication This is when a user is only granted access after successfully presenting multiple, separate pieces of evidence. Typically: Something you know, like a passphrase. Something you have, like a physical token. And/or something you are, like biometric data. Why? Having multiple levels of authentication makes it a lot harder for adversaries to access your information. | Daily backup of important data Regularly back up all data and store it securely offline. Why? That way your organisation can access data again if it suffers a cyber security incident. |